Over the past couple of decades, continuous technological advancement has dramatically increased internet speeds. Broadband and fiber-optic technologies have created blazingly fast networks where even high-definition media can be loaded in surprisingly low time.
There’s yet much more room for improvement in this connection because of the high demand for high-definition media and real-time access to the resources required which are physically kept in the far flung areas on the internet. To iron out internet speed issue is an uphill task and requires various measures to take in an appropriate manner. Changing your DNS settings is often considered as one of the easiest measures to optimize your internet speed. So, let’s take a look at how DNS works and how to change your DNS settings.
What Is Domain Name Service (DNS)?
When you enter a URL for a website or a URI for a resource on the web (html, pdf, excel file, or a media content) into your browser, it needs to be translated into the site’s IP address to send and receive data. The digital cyber world recognizes the machines and devices through their assigned IP addresses.
Now if you enter say www.yahoo.com into your browser’s address bar, your DNS (Domain Name System) server translates that URL or hostname into an IP address – like 123.456.789.12. With over a billion websites and other resources connected on the internet, it isn’t practical to maintain a list that large on a singe DNS server. So instead, your DNS server stores a cache of the most recently requested websites through this DNS server.
If you try to access a website that isn’t already cached, then your configured DNS server will request the entry from another server, which may contain more entries. Your default DNS server is likely to be provided by your ISP and isn’t guaranteed to be the best performing server.
How Does Your Location Affect DNS Speed?
The internet infrastructure is a series of copper and optic-fiber cables connecting servers across the entire globe. Data, that is text, images, audio and video content etc. traverses through these cables in the form of electromagnetic waves, with extremely high speed – the speed of light. While we can’t do anything to further increase that speed, we can reduce the distance these waves have to traverse.
Physical location of the DNS server from the user’s computer who is surfing the internet, substantially affects the internet speed on their computer. Nonetheless, the reality of the internet is more complicated than simple distance calculations that people normally perceive. Google rose to the occasion to resolve this issue for millions of users by providing Public DNS as one of the most popular DNS server alternatives. It provides DNS servers having two IP addresses – 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4.
Having multiple DNS servers all across the globe to provide super-efficient access to the millions of website google’s Public DNS servers have made the lives a lot easier of both web surfers and the website owners. According to Wikipedia “As of 2018, it is the largest public DNS service in the world, handling over a trillion queries per day.”
Google Public DNS service offers support DNS over HTTPS and DNS over TLS – both ones are encrypted transport protocols. These protocols prevent tampering and spoofing, to greatly enhance privacy and security between the client and Google Public DNS.
These DNS servers responding to the requests vary throughout the day, depending on the network traffic and other conditions. Google Public DNS is consistently ranked as one of the fastest DNS servers.
Other than Google Public DNS servers there are several other popular DNS servers which provide blazingly fast access to the internet. In order to help you figure out the best DNS servers for your location here are the most commonly used DNS speed test providers:
NameBench
https://code.google.com/archive/p/namebench/downloads
DNS Jumper
https://www.sordum.org/7952/dns-jumper-v2-2/
GRC Domain Name Speed Benchmark
https://www.grc.com/dns/benchmark.htm
How to Change DNS Settings on Your Computer
The DNS configuration provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is not always the fastest option. You may choose to configure some other Public DNS server like Google Public DNS service. Yet there’re three prominent alternate DNS services providers; Google DNS, Cloudflare DNS, and OpenDNS.
To Change Your DNS on Windows 10
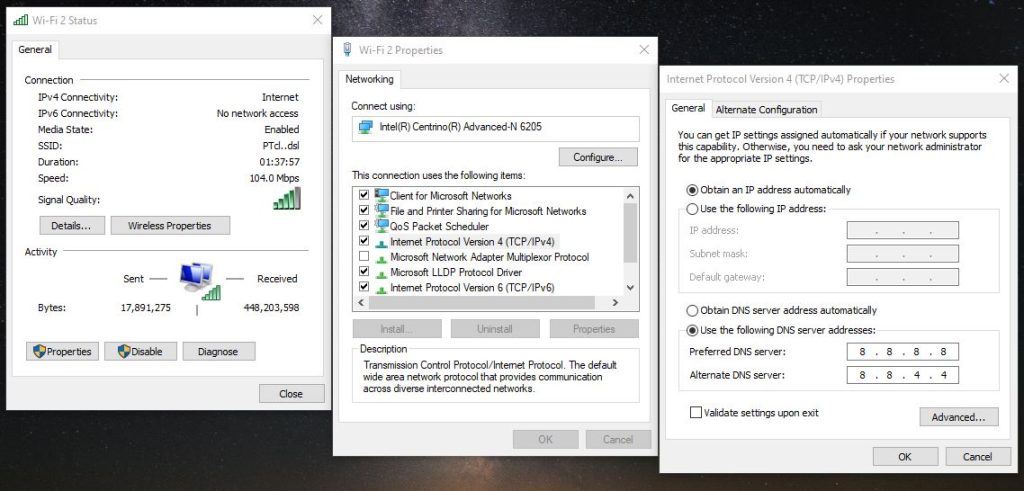
- Press [Win] + X key combination to open the Power User Menu on the bottom-right corner, and select Network Connections.
- Beneath Advanced network settings, select Change adapter options.
- In the new window displaying your available network devices, right-click your internet-connected device and select Properties.
- From the selected network properties locate and click Internet Protocole Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), then click Properties button below.
- Click Use the following DNS server addresses radio option and provide your desired DNS’s IP addresses. In our example we enter Google’s Public DNS servers’ IP addresses.
DNS IP addresses provided by three most common Public DNS providers are as below:
Google DNS: 8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4
Cloudflare IPv4: 1.1.1.1, 1.0.0.1
OpenDNS: 208.67. 222.222, 208.67. 220.220
To Change Your DNS on Windows 11
- Press [Win] + X key combination to open the Power User Menu on the bottom-right corner, and select Network Connections.
- Select Advanced network settings > More network adapter options.
- In the new window displaying your available network devices, right-click your internet-connected device and select Properties.
- Now follow the same instructions as depicted above.
You may also need to setup IPv6. It’s pretty straight forward if you’ve successfully completed IPv4 setup. Just click Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) and click
Properties button.
Again DNS IPv6 addresses provided by the above three Public DNS providers are as below:
Google DNS: 2001:4860:4860::8888, 2001:4860:4860::8844
Cloudflare DNS: 2606:4700:4700::1111, 2606:4700:4700::1001
OpenDNS: 2620:119:35::35, 2620:119:53::53
How to Change DNS Settings on MacOS
To change your DNS on a macOS system:
- Open System Preferences.
- Click Network > Advanced.
- Navigate to the DNS tab.
- Unlike on Windows, you can easily add and remove DNS servers using the “+” and “-” buttons on the window’s bottom left. Once you’ve clicked the + icon, you can enter the IP address of your required DNS provider.
Does Change of DNS Can Substantially Increase Internet Speed?
While there’s no all-embracing solution to improve internet speed, you can take some careful measures and perform tweaks to ensure substantial improvement. These improvements work in conjunction to increase your overall internet speed.
The DNS server(s) you choose, in this regard, are likely to play an essential role. The cool performing DNS servers can substantially reduce the time-lapse in getting the IP addresses of the desired resources on the internet. Therefor, most of the time you’re better off opting for a fast performing yet trust-able DNS server like Google Public DNS.



